Securing Your Digital Empire: AWS Disaster Recovery Guide
Today, businesses rely heavily on data and technology for their day-to-day operations. Any disruption, whether due to natural disasters, cyber-attacks, or system failures, can lead to significant financial loss, damage to reputation, and operational downtime. Hence, having a robust disaster recovery plan is crucial to ensuring business continuity and data protection.
This blog aims to provide a comprehensive guide on AWS Disaster Recovery, helping you understand its importance, explore the various options available, and learn how to implement and manage an effective disaster recovery strategy using AWS.
Understanding AWS Disaster Recovery
Disaster recovery encapsulates a set of policies, tools, and procedures designed to enable the recovery or continuation of vital technology infrastructure and systems following a natural or human-induced disaster. It focuses on restoring data, applications, and IT resources to minimize downtime and mitigate data loss.
AWS offers a range of disaster recovery services tailored to meet different business needs. These services ensure that your data and applications are safe and can be quickly restored in an emergency. AWS’s scalable and reliable infrastructure provides a solid foundation for implementing a disaster recovery plan.
Risks of Not Having a Disaster Recovery Plan
Without a disaster recovery plan, businesses are vulnerable to several risks, including:
- Data Loss:
The absence of a disaster recovery plan puts critical business data at risk of permanent loss. This includes customer information, financial records, and intellectual property. Irretrievable data can cripple operations, hinder decision-making, and lead to costly delays in resuming normal business functions. - Downtime:
Without a structured recovery plan, businesses may experience extended periods of downtime during a disaster. Prolonged inactivity not only disrupts daily operations but also affects overall productivity and can lead to significant revenue loss. The longer the downtime, the greater the negative impact on the company’s ability to serve its customers and meet its operational goals. - Financial Loss:
The financial implications of not having a disaster recovery plan can be severe. Direct costs include loss of income during downtime, while indirect costs encompass long-term financial consequences such as loss of customer trust, decreased market share, and potential loss of future business opportunities. Additionally, emergency response and recovery efforts can incur substantial unexpected expenses. - Reputational Damage:
Inadequate disaster recovery planning can lead to reputational harm as customers and stakeholders lose confidence in the company’s ability to manage and protect their information. Reputational damage can result in decreased customer loyalty, negative media coverage, and a diminished brand image, which may have lasting effects on the business’s market position and customer base. - Regulatory Non-compliance:
Many industries are subject to regulatory requirements concerning data protection and business continuity. Failure to implement a disaster recovery plan can result in non-compliance with these regulations, leading to legal repercussions, including fines and sanctions. Additionally, regulatory bodies may impose stricter oversight, further complicating business operations.
Traditional Disaster Recovery vs. Cloud-Based Disaster Recovery
Traditional Disaster Recovery (DR)
- Infrastructure Requirements:
Traditional DR often relies on dedicated physical infrastructure that mirrors the primary data center. This involves setting up a secondary site with hardware and software similar to the primary site, which can be costly and complex to maintain. - Cost:
The initial investment in traditional DR is typically high due to the need for redundant hardware, real estate, and facilities. Ongoing maintenance costs also add to the financial burden, including power, cooling, and physical security. - Recovery Time Objective (RTO):
Traditional DR may have longer RTOs due to the time required to activate and synchronize the secondary site. The process involves manual intervention and can be slow, impacting the speed of recovery. - Scalability:
Scaling traditional DR solutions often requires significant physical and financial resources. Expanding capacity involves purchasing additional hardware and managing physical space, which can be cumbersome and inflexible. - Maintenance and Management:
Managing traditional DR solutions involves regular testing, updates, and maintenance of physical infrastructure. This requires dedicated IT staff and resources to ensure that the secondary site remains operational and up-to-date. - Complexity:
The complexity of traditional DR setups can be high, requiring intricate planning and coordination to ensure that all systems, applications, and data are adequately replicated and can be quickly restored.
Cloud-Based Disaster Recovery (DR)
- Infrastructure Requirements:
Cloud-based DR leverages virtualized infrastructure provided by cloud service providers. This eliminates the need for a secondary physical site, as data and applications are replicated in the cloud, offering a more flexible and scalable solution. - Cost:
Cloud-based DR typically involves a pay-as-you-go pricing model, reducing the need for large upfront investments. Costs are based on actual usage, including storage and compute resources, making it a more cost-effective option compared to traditional DR. - Recovery Time Objective (RTO):
Cloud-based DR often provides faster RTOs due to automated recovery processes and the ability to quickly access replicated data and applications. Cloud services can often be activated with minimal manual intervention, speeding up the recovery process. - Scalability:
Cloud-based DR solutions offer high scalability, allowing businesses to easily adjust their DR resources based on current needs. Expanding or contracting capacity is straightforward and can be done without significant investment in physical infrastructure. - Maintenance and Management:
Cloud-based DR reduces the burden of maintenance and management, as cloud service providers handle infrastructure updates, security, and availability. This allows businesses to focus on their core operations rather than managing physical DR infrastructure. - Complexity:
While cloud-based DR simplifies many aspects of disaster recovery, it requires a different approach to planning and implementation. Businesses must adapt to cloud-based tools and processes, but overall complexity is often reduced compared to traditional DR.
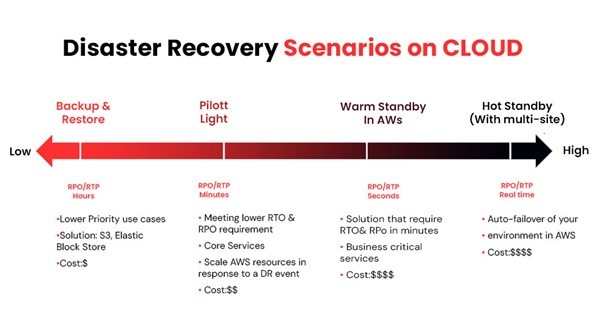
AWS Disaster Recovery Options
Backup and Restore
- Description: Data is regularly backed up to AWS storage services like S3 and restored when needed.
- Pros: Cost-effective, simple to implement.
- Cons: Longer recovery time.
Pilot Light
- Description: A minimal version of the critical environment is always running in AWS, ready to scale up when needed.
- Pros: Faster recovery than Backup and Restore, cost-effective.
- Cons: More complex to manage.
Warm Standby
- Description: A scaled-down version of a fully functional environment is always running in AWS.
- Pros: Reduced recovery time, balance between cost and readiness.
- Cons: Higher cost than Pilot Light.
Multi-Site
- Description: Fully functional and up-to-date environments run simultaneously in different locations.
- Pros: Minimal recovery time, high availability.
- Cons: Most expensive option, complex setup.
Setting Up AWS Disaster Recovery
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up Disaster Recovery on AWS
- Assess Your Needs: Determine the criticality of your applications and data.
- Choose a Recovery Option: Select the most suitable AWS disaster recovery option based on your needs.
- Configure AWS Services: Set up necessary AWS services (e.g., S3 for Backup and Restore, EC2 for Warm Standby).
- Implement Security Measures: Ensure data encryption, access controls, and other security measures.
- Test Your Plan: Regularly test your disaster recovery plan to ensure it works as expected.
- Monitor and Optimize: Continuously monitor performance and make necessary adjustments.
Understanding the Cost Implications of AWS Disaster Recovery
The cost of AWS disaster recovery varies based on the chosen strategy. While Backup and Restore are the most cost-effective, Multi-Site is the most expensive due to its high availability and redundancy. Balancing cost with the desired recovery objectives and business requirements is essential.
Best Practices for AWS Disaster Recovery
- Regular Backups: Ensure frequent backups to minimize data loss.
- Automated Failover: Implement automated failover mechanisms to reduce downtime.
- Security Measures: Protect your data with encryption and secure access controls.
- Regular Testing: Conduct regular disaster recovery drills to validate the plan.
- Documentation: Maintain thorough documentation of your disaster recovery procedures.
Why Choose Rapyder?
Rapyder is exceptionally equipped to guide you through the AWS Disaster Recovery process. Our expertise in AWS Disaster Recovery solutions is tailored to meet your specific needs, ensuring a customized approach to protect your digital assets.
Our team of certified AWS professionals will collaborate with you to build, implement, and maintain a comprehensive disaster recovery plan. With Rapyder, you can confidently secure your business against potential disruptions and ensure uninterrupted operations.
Conclusion
AWS Disaster Recovery provides a robust solution to safeguard your data and applications, ensuring business continuity. By understanding the available options, implementing best practices, and regularly testing your plan, you can build a resilient digital infrastructure that withstands disruptions and maintains operational integrity.
Start exploring AWS Disaster Recovery with Rapyder today to secure your business against any potential disruptions.