13 Cloud Computing Vulnerabilities & How to Manage Them
Cloud computing vulnerabilities refer to weaknesses in cloud systems, services or configurations that attackers can exploit to gain unauthorized access with bad intentions, such as disrupting operations or compromising data integrity. As cloud adoption increases, addressing these vulnerabilities is key to ensuring cloud security and protecting sensitive data.
Some of the most severe impacts of cloud computing vulnerabilities include significant data breaches that lead to financial losses, reputational damage and legal consequences. IT Governance reported numerous incidents in 2023, highlighting the pervasive landscape.
For instance, 867 million records were compromised in October 2023 alone, according to research done by IT Governance. incidents span various sectors, which emphasizes the ubiquitous risk of data exposure. These incidents underline the critical necessity of robust security measures to safeguard cloud environments against such vulnerabilities and mitigate the associated repercussions.
Examples of cloud computing vulnerabilities include insecure APIs, misconfigurations, account hijacking, malicious insiders, DDoS attacks, poor access management, system vulnerabilities, compliance violations, data privacy concerns, lack of visibility, cloud malware injection attacks, lack of encryption and zero-days. We describe each of these cloud vulnerabilities in the sections below.
- Insecure APIs: Weak or poorly designed interfaces that attackers can exploit.
- Misconfigurations: Incorrect settings in cloud services that create security holes.
- Account hijacking: Unauthorized access to user accounts through hacking methods.
- Malicious insiders: Employees who misuse their access to harm the organization.
- DDoS attack: Overloading a service with too much traffic to make it crash.
- Poor access management: Not properly controlling who can use cloud resources.
- System vulnerabilities: Weaknesses in software or hardware that attackers can use.
- Compliance violations: Not meeting legal or regulatory standards in cloud environments.
- Data privacy: Risk of unauthorized access or exposure of personal information.
- Lack of visibility: Not being able to monitor and understand cloud operations well.
- Cloud malware injection attacks: Inserting malicious code into cloud services.
- Lack of encryption: Not protecting data, making it easy to intercept.
- Zero-days: Newly discovered weaknesses that have not yet been fixed.
1. Insecure APIs In Cloud Computing
APIs, or application programming interfaces, are tools that allow unrelated software applications to communicate with each other. Insecure APIs in cloud computing refer to the vulnerabilities or weaknesses in a cloud application’s APIs that can be exploited for unauthorized access or manipulation.
Visual representation of data flow in a web API connecting the API consumer to the database endpoint.
These cloud security vulnerabilities often arise due to poor design, implementation flaws or lack of proper security testing and validation. Insecure APIs can lead to severe issues, such as data breaches, unauthorized access, service disruptions or system compromises, as attackers may bypass security measures, perform unauthorized operations or gain elevated privileges.
For example, Uber suffered a significant data breach in 2016 due to an insecure API, exposing more than 57 million users’ personal information. Attackers accessed Uber’s AWS storage by stealing credentials from a private GitHub repository, allowing them to impersonate legitimate users and access sensitive data in an AWS S3 bucket.
2. Misconfigurations
Misconfigurations refer to incorrect or insecure cloud service settings or deployments of storage buckets, databases, virtual machines or network components. These vulnerabilities exist due to human error, lack of sufficient knowledge or insufficient security controls during configuration and deployment processes.
Misconfiguration vulnerabilities can occur in the following ways:
- Misconfigured cloud storage: Misconfigured settings or configurations of cloud storage services such as Amazon S3 bucket or Azure Blob Storage can lead to unauthorized access or data exposure.
- Bad network configuration: Misconfigured network settings such as virtual private clouds (VPCs), security groups or firewalls can leave cloud resources exposed to unauthorized access or attacks.
- Open S3 bucket: Publicly accessible Amazon S3 buckets without proper access controls can allow anyone to access, modify or delete the stored data.
Misconfigurations in cloud settings, like a poorly configured Amazon S3 bucket left public, can lead to serious security issues, such as data breaches, unauthorized access or service disruptions. These gaps can also result in compliance violations.
For instance, Attunity mistakenly exposed more than a terabyte of sensitive data in May 2019 by leaving three Amazon S3 buckets public. This oversight compromised major firms like Netflix, TD Bank and Ford, revealing internal documents, system passwords and employee details.
3. Account Hijacking
Account hijacking is a type of attack that involves an attacker gaining unauthorized access to a user’s cloud account by stealing or cracking credentials such as usernames and passwords. This vulnerability exists due to weak or compromised authentication mechanisms, lack of multi-factor authentication and successful social engineering attacks.
The following are some of the ways account hijacking vulnerabilities can occur:
- Phishing: Attackers use deceptive emails, messages or websites to trick users into revealing their credentials.
- Brute force attack: This attack involves repeated attempts to guess passwords until the correct one is discovered.
- Keystroke logging: This method involves recording each key that is pressed on a keyboard to capture sensitive information.
- Cross-site scripting: This refers to injecting malicious scripts into websites to steal user credentials or session tokens.
Account hijacking can have severe consequences, as attackers gain full control over compromised accounts and their resources. This can lead to data theft, service disruptions, unauthorized access to sensitive information and further attacks within the cloud.
For example, on Sept. 15, 2022, a hacker used a phishing attack to trick an Uber employee into revealing their password, gaining access to Uber’s internal systems, including email, cloud storage and code repositories.
4. Malicious Insiders
Malicious insiders are individuals with legitimate access to an organization’s cloud resources, such as employees, contractors or third-party vendors, who intentionally misuse their privileges for malicious purposes such as data theft. This vulnerability arises due to a lack of proper access controls, monitoring and security awareness within the organization.
Data breaches, intellectual property theft, service disruptions and reputation damage are some of the potential consequences of malicious insider action. Insiders with elevated access privileges to sensitive information can cause significant harm to the organization’s cloud environment and operations.
A real-life scenario occurred in 2022 when a research scientist at Yahoo stole proprietary information about Yahoo’s AdLearn product and sent the information to his email account minutes after receiving notice of termination.
5. DDoS Attack
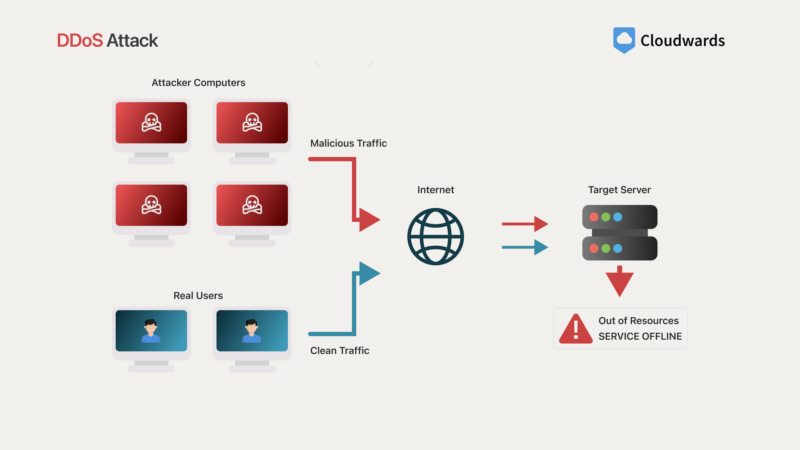
Malicious traffic from a DDoS attack impacts a server by drowning out all other requests.
A distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack is a type of cyberattack that aims to overwhelm a cloud service or application with a large volume of traffic or requests, rendering it inaccessible or disrupting its normal operations. These attacks are often orchestrated using botnets, which are networks of compromised devices controlled by attackers.
The potential effects of DDoS attacks are service disruptions, financial losses due to downtime and reputation damage. DDoS attacks can be used as a form of extortion, where attackers demand ransom payments to stop the attack, or as a means to cause widespread disruption and chaos.
In July 2023, Cloudflare, a major content delivery network and DDoS mitigation provider, was hit by a massive DDoS attack that peaked at 26 million requests per second. The attack targeted one of Cloudflare’s customers, a cryptocurrency exchange service, in an attempt to disrupt its operations.
6. Poor Access Management
Poor access management refers to inadequate controls or practices for granting, monitoring and revoking access to cloud resources. This vulnerability often arises due to a lack of strong identity and access management (IAM) policies, weak authentication mechanisms and insufficient oversight of user privileges.
Common causes of poor access management include:
- Improper identity and access management: Failure to properly manage user accounts, roles and permissions can lead to unauthorized access or excessive privileges.
- Improper authentication: Using weak or outdated authentication methods, such as single-factor authentication or easily guessable passwords, increases the risk of compromised accounts.
- Lack of multi-factor authentication: Not implementing additional authentication layers, like biometrics or one-time codes, makes it easier for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
- Unauthorized access: Granting access to cloud resources without proper verification or following the principle of least privilege can enable potential data misuse or breaches.
The potential effects of poor access management include data breaches, unauthorized access to sensitive information, service disruptions and compliance violations. Inadequate access controls can also facilitate insider threats and malicious activity in cloud environments.
In July 2019, Capital One suffered a major data breach. A hacker gained access to the personal information of more than 100 million Capital One credit card applicants and customers in the U.S. and Canada. The breach occurred after a former Amazon employee managed to exploit a misconfigured web application firewall on Capital One’s cloud infrastructure hosted on AWS.
7. System Vulnerabilities
System vulnerabilities are weaknesses in the underlying software, operating systems or hardware components used in cloud computing environments. These vulnerabilities can arise due to unpatched systems, outdated software versions or inherent design flaws in the technology stack.
The effects of system vulnerabilities include potential exploitation by attackers to gain unauthorized access, execute malicious code or compromise the confidentiality, integrity or availability of cloud resources. Unpatched vulnerabilities can provide entry points for attackers to infiltrate the cloud environment and potentially compromise other connected systems.
8. Compliance Violations
Compliance violations occur when an organization fails to adhere to relevant industry regulations, standards or legal requirements related to data privacy, security or other aspects of cloud computing. These violations can arise due to a lack of awareness, inadequate security controls or insufficient governance and oversight within the organization.

The GDPR is made up of seven core principles that all organizations that handle user data must follow.
Possible consequences of noncompliance include regulatory fines, legal liabilities, reputation damage and loss of customer trust. Failure to comply with data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) can result in significant financial penalties and legal consequences.
9. Data Privacy
Data privacy vulnerabilities occur when protective measures fail to safeguard personal and sensitive information stored on cloud systems due to insufficient data protection policies, a lack of strong encryption or inadequate access controls. The effects can be severe, including identity theft, financial loss for individuals and organizations, and damage to a company’s reputation.
A real-life example of such a vulnerability took place in 2020 when hackers breached Blackbaud, a company that provides cloud-based CRM tools to NGOs and institutions. This breach affected many educational and nonprofit organizations around the world, as hackers accessed sensitive data and held it for ransom.
10. Lack of Visibility
Lack of visibility is a vulnerability that arises when organizations cannot see or understand what is happening within their cloud environments. This usually happens because of inadequate monitoring tools or insufficient procedures to track cloud operations.
The effects of this can be serious, as it may lead to unnoticed security breaches, missed compliance issues or operational inefficiencies. An example of a security incident that occurred due to a lack of visibility is the Verizon data breach. A misconfigured AWS S3 bucket in Verizon’s cloud environment led to the exposure of six million customers’ personal information.
11. Cloud Malware Injection Attacks
Cloud malware injection attacks happen when hackers insert malicious software into a cloud system. This can occur due to weak security measures or vulnerabilities in the cloud software that hackers exploit. The effects of such attacks can be severe, including data theft, unauthorized system control and service disruption.
An example of cloud malware injection is the Tesla crypto-jacking incident from 2018, when attackers exploited a misconfigured Kubernetes console in Tesla’s AWS cloud environment to deploy crypto-mining malware.
12. Lack of Encryption
Lack of encryption is the failure to implement adequate encryption mechanisms to protect sensitive data in transit or at rest within cloud environments. It can occur due to oversight, lack of awareness or improper implementation. Lack of encryption leaves sensitive data vulnerable to interception, unauthorized access or theft during transmission or storage in the cloud.
The 2017 Equifax data breach occurred due to a lack of encryption. Hackers exploited a vulnerability in the web application to gain access. The lack of encryption allowed them to easily view and steal roughly 147 million Americans’ sensitive personally identifiable information. This included names, social security numbers, birth dates, addresses and driver’s license numbers.
13. Zero-Days
Zero-day vulnerabilities are unknown flaws in software that haven’t been fixed yet because the developers themselves don’t know about them. They are called “zero-days” because developers have no time to fix them before they can be exploited.
These flaws usually emerge because not all parts of complex software are fully tested. The effects can be serious, such as allowing attackers to access data, take control of systems and cause major disruptions. These vulnerabilities can lead to big security problems because organizations aren’t prepared for them.
In March 2021, Microsoft disclosed multiple zero-day vulnerabilities in on-premises versions of Microsoft Exchange Server that a state-sponsored hacking group called Hafnium — believed to be operating out of China — was actively exploiting. The threat actors used the vulnerabilities to gain access to Exchange servers and compromise thousands of organizations worldwide.
Understanding: What Is Cloud Computing Vulnerability Management?
Cloud computing vulnerability management is the process of identifying, assessing and mitigating vulnerabilities in cloud environments. It helps organizations reduce risks and enhance the security of their cloud infrastructure, applications and data. A cloud vulnerability assessment is conducted to identify potential flaws or weaknesses in the cloud environment.
What Is the Difference Between Cloud Computing Vulnerabilities and Cloud Computing Threats?
A cloud computing vulnerability is a potential weakness, such as an insecure API or misconfigured storage bucket, that has not been exploited. Cloud computing threats occur when attackers exploit a vulnerability to gain access and breach the system. For example, a malicious actor could exploit a zero-day vulnerability or access privileges to harm a system.
Final Thoughts
We’ve discussed important issues related to cloud computing vulnerabilities and security threats, and emphasized the importance of implementing strong security measures. Cloud computing vulnerabilities can have severe consequences, ranging from data breaches and service disruptions to compliance violations and damage to reputations.
However, by implementing strong security measures, conducting regular vulnerability assessments and following industry best practices, organizations can effectively manage and mitigate these vulnerabilities as well as overcome other cloud computing challenges.
We would love to hear about your experience with cloud computing vulnerabilities. How do you handle these challenges in your cloud setups? Feel free to share your strategies and questions in the comments below. Thanks for reading, and let’s continue working together to keep our cloud environments secure!
FAQ: Cloud Vulnerabilities